What are the CIA Triad | Foundation of Cybersecurity Principles
In today’s digital world, where data flows freely and cyber threats lurk around every corner, protecting information is more critical than ever. Whether you’re a business owner safeguarding customer data, an IT professional securing a network, or simply someone browsing the internet, understanding the core principles of cybersecurity is essential. At the heart of these principles lies the CIA Triad—a simple yet powerful framework that guides how we protect information. The triad stands for Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability. These three pillars form the foundation of cybersecurity, ensuring that data remains secure, accurate, and accessible when needed. Think of the CIA Triad as the blueprint for keeping your digital world safe. Just as a house needs a strong foundation to withstand storms, your data needs these three elements to stay protected from cyber threats. In this blog post, we’ll dive deep into the CIA Triad, breaking down each component, exploring real-world applications, and answering common questions to help you understand why it’s so important. Whether you’re new to cybersecurity or looking to refresh your knowledge, this guide will make the concepts clear and actionable.
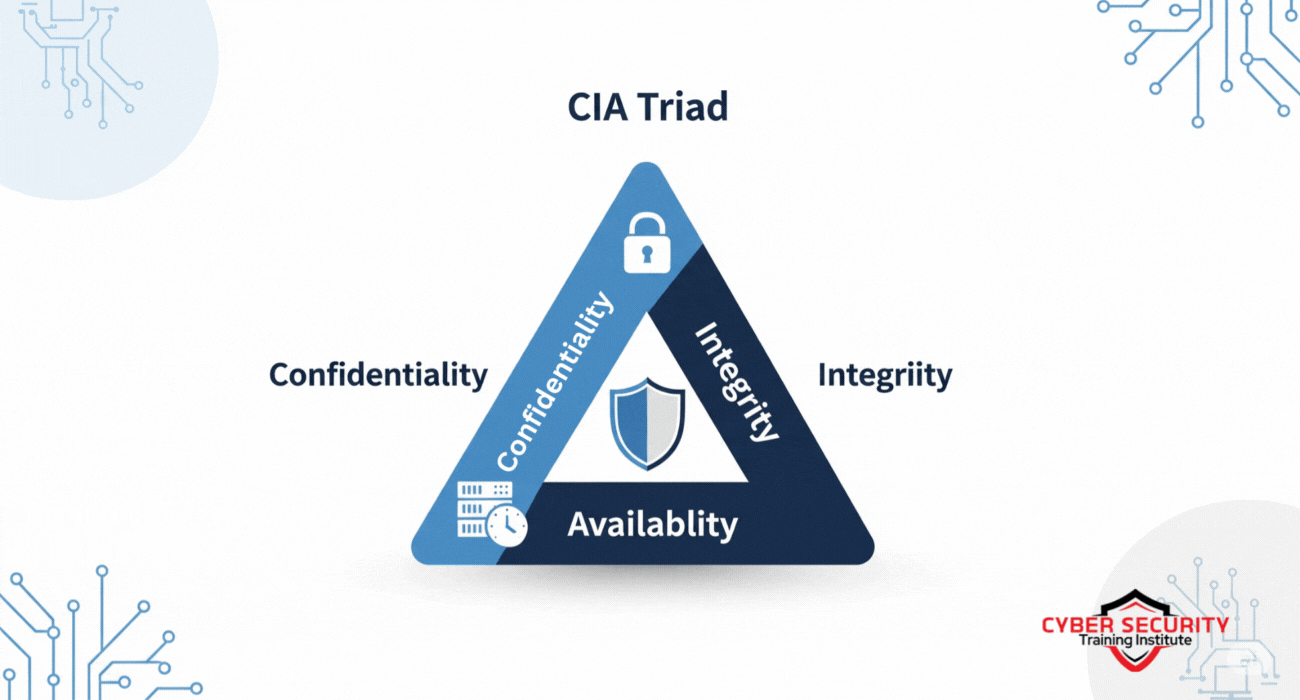
Table of Contents
- What is the CIA Triad?
- Confidentiality: Keeping Data Private
- Integrity: Ensuring Data Accuracy
- Availability: Making Data Accessible
- Balancing the Triad
- Real-World Applications of the CIA Triad
- Challenges in Implementing the CIA Triad
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
What is the CIA Triad?
The CIA Triad is a model used in cybersecurity to guide the protection of information. It’s not about the Central Intelligence Agency (despite the acronym!) but rather a framework that focuses on three key principles: Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability. These principles work together to ensure that data is secure, trustworthy, and available to the right people at the right time.
Imagine the CIA Triad as a three-legged stool. If one leg is weak or missing, the stool becomes unstable, and your data’s security is at risk. By addressing all three components, organizations and individuals can create a robust defense against cyber threats like hacking, data breaches, and system failures.
Here’s a quick overview of the triad:
| Component | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Confidentiality | Ensures data is only accessed by authorized individuals. | Encrypting sensitive emails. |
| Integrity | Guarantees data is accurate and unaltered. | Using checksums to verify file integrity. |
| Availability | Ensures data and systems are accessible when needed. | Implementing backup servers to prevent downtime. |
Confidentiality: Keeping Data Private
Confidentiality is all about ensuring that data is only accessible to those who are authorized to see it. Think of it like locking your diary with a key—only you (or someone you trust with the key) can read its contents. In the digital world, confidentiality prevents sensitive information, like personal details, financial records, or trade secrets, from falling into the wrong hands.
How is confidentiality achieved?
- Encryption: This scrambles data so only those with the decryption key can read it. For example, when you see “https” in a website’s URL, encryption is protecting your data.
- Access Controls: Passwords, biometrics (like fingerprint scans), and multi-factor authentication (MFA) ensure only authorized users can access systems.
- Data Masking: This hides parts of sensitive data, like showing only the last four digits of a credit card number.
Real-world example: A hospital uses encryption to protect patient records. Only doctors and authorized staff with proper credentials can access medical histories, keeping them safe from hackers or unauthorized employees.
Threats to confidentiality: Hackers might use phishing attacks to steal login credentials or exploit software vulnerabilities to access sensitive data. Breaches, like the 2017 Equifax incident where personal data of millions was exposed, highlight the importance of strong confidentiality measures.
Integrity: Ensuring Data Accuracy
Integrity ensures that data remains accurate, complete, and unaltered unless authorized. Imagine sending a letter and knowing it hasn’t been tampered with before it reaches the recipient. In cybersecurity, integrity means your data hasn’t been modified by hackers, corrupted by errors, or changed without permission.
How is integrity maintained?
- Hashing: A hash function generates a unique code (or “hash”) for a piece of data. If the data changes, the hash won’t match, signaling tampering.
- Digital Signatures: These verify that a message or file comes from a trusted source and hasn’t been altered.
- Version Control: Systems like Git track changes to files, ensuring only authorized updates are made.
Real-world example: A bank uses hashing to ensure that transaction records aren’t altered. If a hacker tries to change a $100 transfer to $10,000, the hash mismatch would flag the issue.
Threats to integrity: Malware, like ransomware, can alter or corrupt data. Human errors, such as accidentally deleting files, can also compromise integrity. Regular backups and checksums help mitigate these risks.
Availability: Making Data Accessible
Availability ensures that data and systems are accessible to authorized users when they need them. It’s like making sure your favorite coffee shop is open when you’re craving a latte. In cybersecurity, availability means systems are up and running, and data can be retrieved without delays or disruptions.
How is availability ensured?
- Redundancy: Backup servers or cloud storage ensure systems stay online even if one server fails.
- Firewalls and DDoS Protection: These defend against Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attacks that overwhelm systems and make them unavailable.
- Regular Maintenance: Updating software and patching vulnerabilities prevent downtime caused by exploits.
Real-world example: An e-commerce website uses load balancers to distribute traffic across multiple servers, ensuring the site stays online during a Black Friday sale.
Threats to availability: DDoS attacks, power outages, or hardware failures can disrupt access. For instance, the 2020 Twitter hack, where high-profile accounts were compromised, temporarily affected the platform’s availability for some users.
Balancing the Triad
While all three components of the CIA Triad are crucial, balancing them can be challenging. Strengthening one aspect might weaken another. For example, adding multiple layers of encryption (confidentiality) could slow down system performance (availability). Similarly, frequent backups (availability) might increase the risk of unauthorized access (confidentiality) if not secured properly.
Organizations must assess their priorities based on their needs. A bank might prioritize confidentiality to protect customer data, while a streaming service might focus on availability to ensure uninterrupted access. The key is to find a balance that minimizes risks without compromising usability.
Real-World Applications of the CIA Triad
The CIA Triad isn’t just a theoretical concept—it’s applied across industries to protect data and systems. Here are a few examples:
- Healthcare: Hospitals use the triad to protect patient records (confidentiality), ensure medical data isn’t altered (integrity), and keep systems like MRI machines operational (availability).
- Finance: Banks rely on the triad to secure transactions, prevent fraud, and ensure customers can access funds anytime.
- E-commerce: Online stores use encryption for payments, verify product listings, and maintain uptime during peak shopping seasons.
- Government: Agencies protect classified information, ensure accurate records, and maintain critical infrastructure like emergency response systems.
Challenges in Implementing the CIA Triad
Implementing the CIA Triad isn’t without hurdles. Some common challenges include:
- Cost: Advanced security measures like encryption or redundant servers can be expensive, especially for small businesses.
- Complexity: Balancing the triad requires expertise, and misconfigurations can lead to vulnerabilities.
- Evolving Threats: Cybercriminals constantly develop new attack methods, requiring ongoing updates to security practices.
- User Error: Employees clicking phishing links or misusing systems can undermine even the best security measures.
To overcome these, organizations invest in employee training, regular audits, and scalable security solutions tailored to their needs.
Conclusion
The CIA Triad—Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability—is the cornerstone of cybersecurity. By ensuring that data is private, accurate, and accessible, the triad provides a clear framework for protecting information in an increasingly connected world. Whether you’re securing a small business, a personal device, or a global enterprise, the principles of the CIA Triad guide you toward robust security practices.
From encryption to backups to DDoS protection, each component of the triad plays a vital role in defending against cyber threats. While challenges like cost and complexity exist, understanding and applying the triad empowers individuals and organizations to stay one step ahead of cybercriminals. By prioritizing these principles, we can build a safer digital future for everyone.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does CIA stand for in cybersecurity?
It stands for Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability, the three core principles of the CIA Triad.
Why is the CIA Triad important?
It provides a framework to protect data by ensuring it’s secure, accurate, and accessible, reducing the risk of breaches or disruptions.
How does encryption support confidentiality?
Encryption scrambles data, making it unreadable to unauthorized users without the decryption key.
What is an example of a confidentiality breach?
A hacker accessing customer data, like credit card numbers, due to weak passwords or unencrypted systems.
How can integrity be compromised?
Integrity can be compromised by malware altering data or human errors like accidental file changes.
What tools help maintain data integrity?
Hashing, digital signatures, and version control systems help ensure data remains accurate and unaltered.
What threatens data availability?
DDoS attacks, hardware failures, or power outages can disrupt access to data and systems.
How do backups improve availability?
Backups ensure data can be restored quickly if systems fail or are compromised.
Can the CIA Triad be applied to personal devices?
Yes, using strong passwords (confidentiality), antivirus software (integrity), and cloud backups (availability) applies the triad to personal devices.
What industries rely on the CIA Triad?
Healthcare, finance, e-commerce, government, and more use the triad to protect sensitive data and systems.
How does multi-factor authentication (MFA) relate to the CIA Triad?
MFA enhances confidentiality by requiring multiple forms of verification to access data.
What is a DDoS attack?
A Distributed Denial-of-Service attack floods a system with traffic to make it unavailable to users.
How do you balance the CIA Triad?
Assess priorities based on needs, like focusing on confidentiality for sensitive data or availability for critical services.
What is data masking?
Data masking hides parts of sensitive data, like showing only the last four digits of a credit card.
How does hashing work?
Hashing generates a unique code for data. If the data changes, the hash won’t match, indicating tampering.
Can the CIA Triad prevent all cyber threats?
No, but it provides a strong framework to reduce risks and guide security practices.
What role does employee training play in the CIA Triad?
Training helps employees avoid mistakes like clicking phishing links, which can compromise confidentiality or integrity.
How do firewalls support the CIA Triad?
Firewalls protect availability by blocking malicious traffic that could disrupt systems.
Why is the CIA Triad called a “triad”?
It’s called a triad because its three components (Confidentiality, Integrity, Availability) work together to ensure security.
Where can I learn more about the CIA Triad?
Check resources from cybersecurity organizations like NIST or online courses from platforms like Coursera.
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0














