What Is Risk Management in Cybersecurity? Concepts and Frameworks Explained
In today’s digital world, where businesses rely heavily on technology, cybersecurity is no longer just a technical issue—it’s a business necessity. Every day, organizations face threats like data breaches, ransomware, and phishing attacks that can disrupt operations, damage reputations, and lead to significant financial losses. This is where risk management in cybersecurity comes into play. It’s a structured approach to identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks to keep your organization safe. Whether you’re a beginner or a seasoned professional, understanding risk management is key to protecting sensitive data and ensuring business continuity. In this blog post, we’ll break down the core concepts of cybersecurity risk management, explore popular frameworks, and provide practical insights to help you navigate this critical field. Let’s dive in!
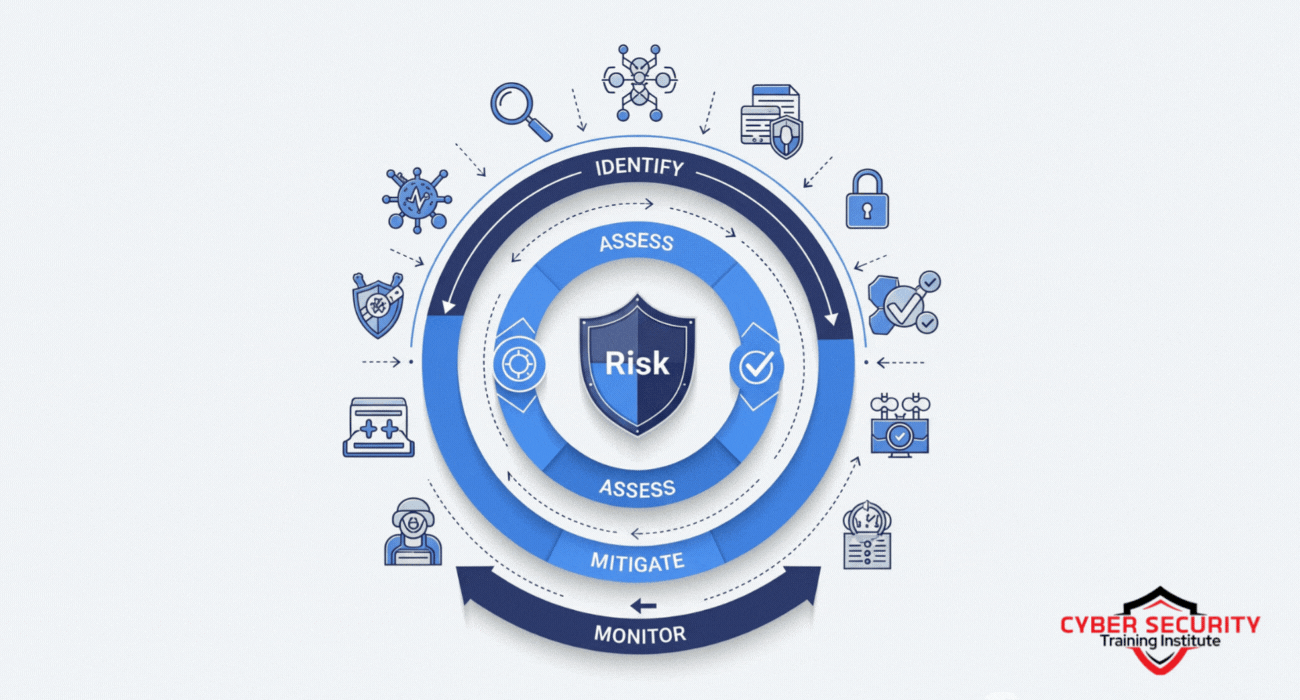
Table of Contents
- What Is Risk Management in Cybersecurity?
- Key Concepts of Cybersecurity Risk Management
- Why Is Risk Management Important?
- Popular Cybersecurity Risk Management Frameworks
- Steps in Cybersecurity Risk Management
- Challenges in Cybersecurity Risk Management
- Best Practices for Effective Risk Management
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What Is Risk Management in Cybersecurity?
Risk management in cybersecurity is the process of identifying, analyzing, and addressing potential risks to an organization’s information systems. It involves understanding what could go wrong, evaluating the likelihood and impact of those events, and taking steps to reduce or eliminate the risks. Think of it as a proactive strategy to protect your digital assets—data, systems, and networks—from threats like hackers, malware, or even human error.
At its core, risk management is about making informed decisions. It’s not about eliminating every possible threat (which is nearly impossible) but about prioritizing risks based on their potential impact and likelihood. By doing so, organizations can focus their resources on the most critical areas, balancing security with operational efficiency.
Key Concepts of Cybersecurity Risk Management
To understand risk management, you need to grasp a few foundational concepts. These are the building blocks that guide the process:
- Threat: Any potential danger to your systems, like a hacker, virus, or natural disaster.
- Vulnerability: A weakness in your systems or processes that a threat could exploit, such as outdated software or weak passwords.
- Risk: The combination of a threat exploiting a vulnerability and the resulting impact, like financial loss or data exposure.
- Likelihood: The probability that a risk will occur.
- Impact: The potential damage if a risk materializes, such as downtime or reputational harm.
- Mitigation: Actions taken to reduce the likelihood or impact of a risk, like installing firewalls or training employees.
These concepts work together to help organizations understand their cybersecurity landscape and make strategic decisions.
Why Is Risk Management Important?
Cybersecurity risks are growing in both frequency and sophistication. According to recent studies, the average cost of a data breach in 2023 was over $4 million, and that number continues to rise. Risk management helps organizations:
- Protect Sensitive Data: Safeguard customer information, intellectual property, and trade secrets.
- Ensure Business Continuity: Minimize disruptions from cyber incidents.
- Comply with Regulations: Meet legal and industry standards, like GDPR or HIPAA.
- Build Trust: Show customers and partners that security is a priority.
- Save Costs: Prevent financial losses from breaches or fines.
Without a risk management strategy, organizations are essentially gambling with their security, leaving themselves vulnerable to unpredictable threats.
Popular Cybersecurity Risk Management Frameworks
A framework provides a structured approach to managing cybersecurity risks. Below is a table summarizing some of the most widely used frameworks:
| Framework | Description | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| NIST Cybersecurity Framework | Developed by the National Institute of Standards and Technology, it provides a flexible approach with five core functions: Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, and Recover. | Organizations of all sizes looking for a customizable framework. |
| ISO/IEC 27001 | An international standard for Information Security Management Systems (ISMS), focusing on risk assessment and continuous improvement. | Businesses seeking global compliance and certification. |
| COBIT | A framework for IT governance and management, emphasizing risk optimization and aligning IT with business goals. | Large enterprises with complex IT environments. |
| CIS Controls | A set of prioritized cybersecurity actions designed to protect against common threats. | Small to medium-sized businesses needing practical guidance. |
Each framework offers unique strengths, and the best choice depends on your organization’s size, industry, and goals.
Steps in Cybersecurity Risk Management
Risk management follows a cyclical process to ensure continuous improvement. Here are the key steps:
- Identify Risks: List all assets (e.g., servers, databases) and potential threats (e.g., malware, insider threats).
- Assess Risks: Evaluate the likelihood and impact of each risk using tools like risk matrices or heatmaps.
- Prioritize Risks: Rank risks based on severity to focus on the most critical ones first.
- Implement Controls: Apply measures like encryption, access controls, or employee training to mitigate risks.
- Monitor and Review: Continuously track risks and controls, adjusting strategies as new threats emerge.
This process ensures that risks are managed systematically, with regular updates to address evolving threats.
Challenges in Cybersecurity Risk Management
While risk management is essential, it’s not without challenges:
- Evolving Threats: Cyber threats change rapidly, making it hard to stay ahead.
- Resource Constraints: Limited budgets and skilled staff can hinder effective risk management.
- Complex Systems: Modern IT environments, with cloud and IoT devices, are harder to secure.
- Human Error: Employees may inadvertently cause breaches through phishing or weak passwords.
- Regulatory Compliance: Keeping up with laws like GDPR or CCPA can be overwhelming.
Addressing these challenges requires a combination of technology, training, and strategic planning.
Best Practices for Effective Risk Management
To build a robust risk management program, consider these best practices:
- Adopt a Framework: Use a framework like NIST or ISO 27001 to guide your efforts.
- Involve Leadership: Ensure executives understand and support cybersecurity initiatives.
- Train Employees: Regular training reduces human-related risks like phishing.
- Use Technology: Leverage tools like firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and encryption.
- Regular Audits: Conduct periodic assessments to identify new risks and gaps.
- Plan for Incidents: Develop and test an incident response plan to minimize damage.
Conclusion
Risk management in cybersecurity is a critical practice for protecting organizations in an increasingly digital world. By understanding threats, vulnerabilities, and risks, and by adopting structured frameworks like NIST or ISO 27001, businesses can safeguard their assets and maintain trust. While challenges like evolving threats and resource constraints exist, following best practices—such as employee training, regular audits, and strong leadership support—can make risk management effective and manageable. Ultimately, a proactive approach to risk management not only prevents costly incidents but also builds resilience for the future.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is cybersecurity risk management?
It’s the process of identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks to an organization’s information systems to protect data and ensure business continuity.
Why is risk management important in cybersecurity?
It helps protect sensitive data, ensures compliance, minimizes disruptions, and saves costs from potential breaches.
What is a cybersecurity threat?
A threat is any potential danger, like a hacker, malware, or natural disaster, that could harm your systems.
What is a vulnerability in cybersecurity?
A vulnerability is a weakness, such as outdated software or weak passwords, that a threat could exploit.
What is a risk in cybersecurity?
A risk is the potential impact of a threat exploiting a vulnerability, like data loss or system downtime.
What are some common cybersecurity risks?
Common risks include data breaches, ransomware, phishing attacks, and insider threats.
What is the NIST Cybersecurity Framework?
A flexible framework with five core functions—Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, Recover—to manage cybersecurity risks.
What is ISO 27001?
An international standard for building an Information Security Management System (ISMS) to manage risks.
How does COBIT differ from NIST?
COBIT focuses on IT governance and aligning IT with business goals, while NIST emphasizes cybersecurity risk management.
What are CIS Controls?
A set of prioritized cybersecurity actions to protect against common threats, ideal for smaller organizations.
How do you identify cybersecurity risks?
List all assets (e.g., servers, data) and potential threats (e.g., hackers, malware) that could affect them.
What is a risk assessment?
A process to evaluate the likelihood and impact of identified risks to prioritize mitigation efforts.
How can you mitigate cybersecurity risks?
Use measures like encryption, firewalls, access controls, and employee training to reduce risks.
What is a risk matrix?
A tool that plots risks based on their likelihood and impact to help prioritize them.
Why do cyber threats keep evolving?
Attackers adapt to new technologies, exploit new vulnerabilities, and use advanced techniques to bypass defenses.
How does employee training help in risk management?
Training reduces human errors, like falling for phishing scams, by teaching employees security best practices.
What role does leadership play in risk management?
Leadership provides resources, sets priorities, and fosters a security-focused culture.
Why are regular audits important?
Audits identify new risks, gaps in controls, and areas for improvement in your security strategy.
What is an incident response plan?
A plan outlining steps to detect, respond to, and recover from cybersecurity incidents to minimize damage.
Can small businesses benefit from risk management?
Yes, risk management helps small businesses protect data, comply with regulations, and avoid costly breaches.
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0
















