Understanding VPNs | How Virtual Private Networks Strengthen Online Privacy and Cybersecurity in 2025
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) play a vital role in modern cybersecurity by encrypting internet traffic, hiding IP addresses, and protecting users on public networks. In this blog, explore how VPNs work, their benefits in preventing data breaches, their real-life use cases, and their limitations. Learn why VPNs are essential for individuals, businesses, and remote workers seeking safe and private online experiences.

Table of Contents
What is a VPN?
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) is a secure technology that creates a protected connection between your device and the internet. It routes your internet traffic through a remote server, making your online actions private, encrypted, and nearly impossible to track.
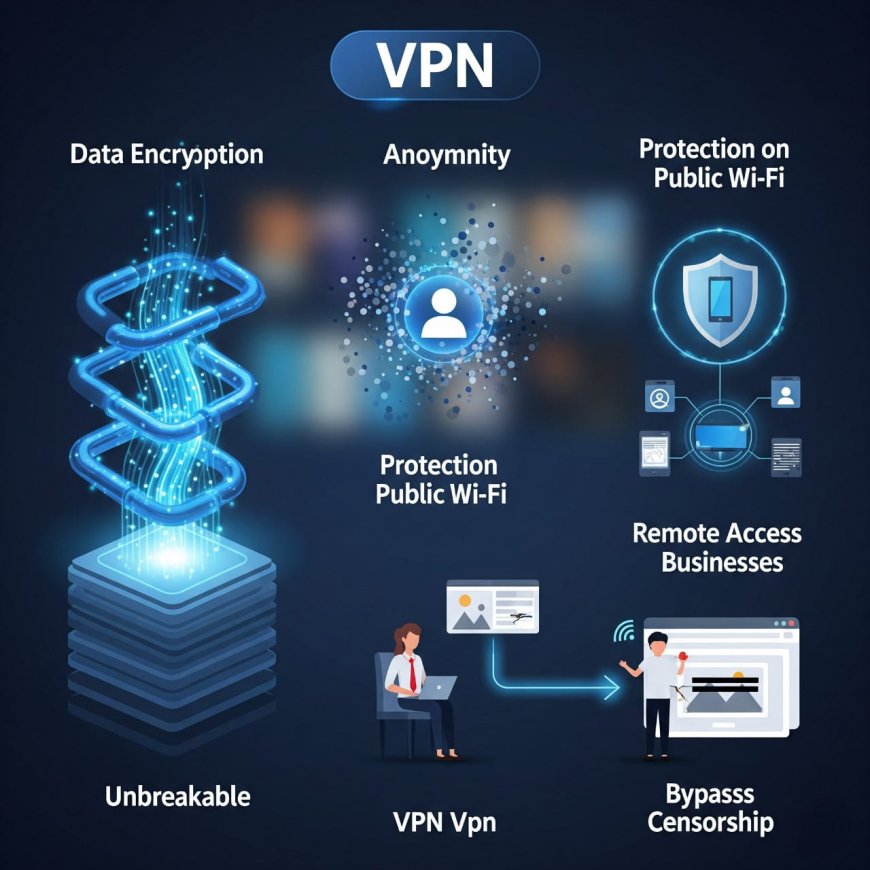
How Does a VPN Work?
When you use a VPN, your internet traffic is encrypted and sent through a secure tunnel to a server managed by the VPN provider. This hides your real IP address, protects your identity, and keeps your data away from prying eyes.
Step-by-Step Process
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | User connects to the internet through a VPN app |
| 2 | The VPN encrypts the data on the user’s device |
| 3 | Encrypted data is sent through a secure tunnel |
| 4 | VPN server decrypts and forwards the request to the internet |
| 5 | Response comes back through the VPN server to the user |
Why VPNs Are Important in Cybersecurity
- Data Encryption: VPNs encrypt internet traffic using strong algorithms like AES-256, making it unreadable to hackers, governments, or ISPs.
- IP Address Masking: By changing your IP address, VPNs hide your location and identity, preventing tracking and surveillance.
- Public Wi-Fi Protection: Using public Wi-Fi at airports, cafes, or hotels? A VPN protects your connection from potential man-in-the-middle attacks.
- Safe Remote Access: Organizations use VPNs to allow employees to securely access internal systems and files while working remotely.
- Firewall Bypass and Censorship: Though not a direct cybersecurity benefit, VPNs help bypass restrictions and allow secure access to blocked content in censored regions.

Limitations of VPNs
While VPNs are powerful tools, they have limitations:
- Do not block viruses or malware
- Free VPNs may track user data or inject ads
- VPN speed may vary depending on server load
- Misconfigured VPNs can leak information (DNS leaks)
Best Practices for Using a VPN Safely
- Choose a reputable, no-log VPN provider
- Always use a VPN on public networks
- Enable the kill switch feature to avoid leaks
- Keep your VPN app updated
- Combine VPN with antivirus and firewall software
Use Cases of VPNs in Real Life
| Use Case | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Remote Work | Secure company data access |
| Travelers | Access geo-restricted content |
| Activists | Bypass surveillance and censorship |
| Students | Safe online learning via public Wi-Fi |
| Gamers | Reduce lag, avoid DDoS attacks |
Conclusion
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) are no longer optional—they're a necessity in a world full of digital threats. From encrypting your connection to providing anonymity, VPNs are a critical layer in your cybersecurity strategy. However, remember: a VPN is just one piece of the puzzle. Use it alongside strong passwords, firewalls, and cybersecurity awareness to stay truly safe.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is a VPN and how does it work?
A VPN encrypts your internet traffic and routes it through a secure server, masking your IP address and location.
Why is a VPN important for cybersecurity?
It protects sensitive data from hackers, especially on public Wi-Fi, and ensures private internet access.
Can VPNs prevent hacking?
While VPNs add protection, they can't fully stop all forms of hacking. They help prevent interception of data.
Are VPNs legal to use?
Yes, VPNs are legal in most countries, though some restrict or regulate them.
Is using a VPN safe?
Yes, using a reputable VPN is safe and can enhance your online security.
Can VPNs protect me on public Wi-Fi?
Absolutely, VPNs encrypt your data, preventing man植物in-the-middle attacks on open networks.
Do VPNs hide my location?
Yes, VPNs mask your real IP address and show the location of the VPN server instead.
Are free VPNs safe to use?
Free VPNs often come with risks such as data logging or slower speeds. Use trusted paid services.
What does a no-log VPN mean?
A no-log VPN does not store any records of your online activity, ensuring better privacy.
Do VPNs slow down internet speed?
Sometimes, depending on the server distance and load, VPNs may reduce speed slightly.
Can VPNs bypass firewalls?
Yes, VPNs can bypass network and country firewalls, giving access to restricted content.
Is a VPN the same as antivirus software?
No, a VPN secures your connection while antivirus protects your device from malware.
Can I use a VPN on my smartphone?
Yes, most VPNs offer mobile apps for both Android and iOS devices.
How do VPNs protect remote workers?
They provide secure access to company networks, protecting internal data from cyber threats.
What protocols do VPNs use?
Common protocols include OpenVPN, IKEv2/IPSec, and WireGuard.
Can VPNs block ads or trackers?
Some premium VPNs offer ad and tracker blocking features.
Will a VPN affect online gaming?
It may slightly increase latency, but it also helps protect against DDoS attacks.
How do I choose the best VPN?
Look for no-log policy, speed, strong encryption, and customer support.
Can a VPN bypass ISP throttling?
Yes, VPNs can hide your traffic from ISPs, which may prevent throttling.
Do VPNs work with streaming services?
Yes, many VPNs can unblock geo-restricted streaming platforms.
Are VPNs used in businesses?
Yes, companies use VPNs to create secure communication channels for remote employees.
Can I leave my VPN on all the time?
Yes, and it’s recommended for continuous protection and privacy.
What is a VPN kill switch?
It automatically disconnects the internet if the VPN drops, preventing data leaks.
Can governments track VPN usage?
They can detect VPN traffic, but not the content or destination of your communication.
What is DNS leak protection in VPNs?
It ensures your DNS queries go through the VPN and not your ISP.
Are VPNs compatible with all devices?
Most major VPNs support Windows, Mac, iOS, Android, Linux, and routers.
How do VPNs support freedom of speech?
They allow access to information and secure communication in censored regions.
What’s the difference between a proxy and a VPN?
VPNs encrypt your traffic; proxies only hide your IP without encryption.
Can I use a VPN in school or college?
Yes, VPNs can bypass campus restrictions, but always follow institution policies.
Do VPNs store browsing history?
Reputable VPNs do not store browsing data if they follow a strict no-logs policy.
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0














