DNS Spoofing Explained | What It Is, How It Works, and How to Protect Yourself
DNS Spoofing, also known as DNS cache poisoning, is a dangerous cyberattack where an attacker redirects your internet traffic by corrupting DNS records. This redirection can lead you to fake websites that steal your personal data, login credentials, or install malware. In this blog, you’ll learn what DNS spoofing is, how it works, real-life examples, and how to identify and prevent it using secure DNS protocols, firewalls, and anti-malware tools. Whether you're an individual or an IT professional, understanding DNS spoofing is essential to protect your online activity from being hijacked by cybercriminals.
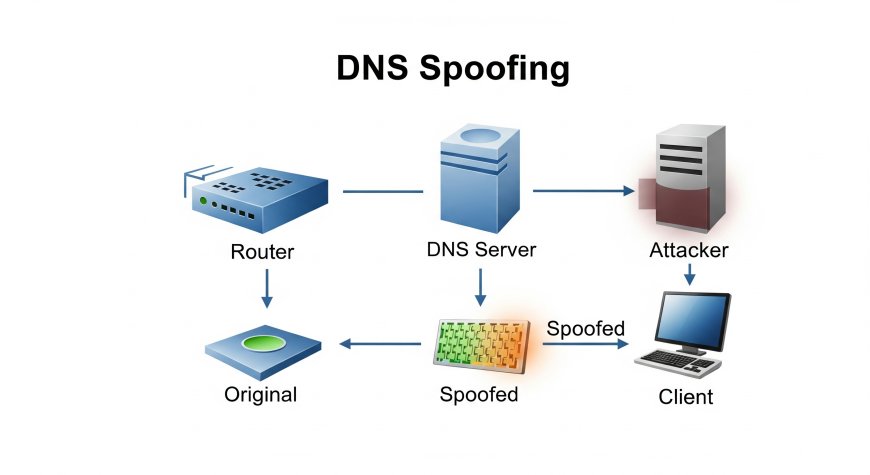
Table of Contents
Introduction
In today's digital age, the Domain Name System (DNS) is a critical component of internet functionality, translating human-readable domain names into machine-readable IP addresses. However, this system is vulnerable to attacks, one of the most insidious being DNS spoofing. This blog explores what DNS spoofing is, how it works, its impact, and how you can protect yourself from it.
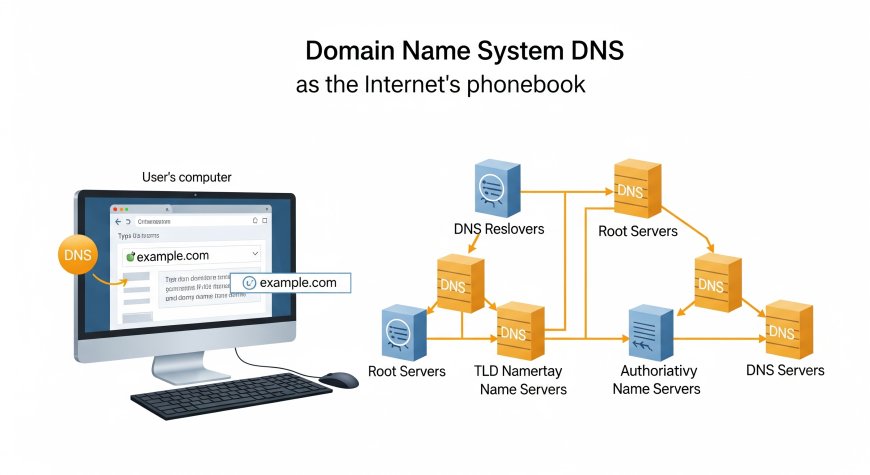
What is DNS?
DNS, or Domain Name System, acts like the internet's phonebook. It converts domain names (e.g., www.example.com) into IP addresses (e.g., 192.0.2.1) that computers use to communicate. Without DNS, browsing the internet would require memorizing complex numerical addresses.
What is DNS Spoofing?
DNS spoofing, also known as DNS cache poisoning, is a cyberattack where an attacker manipulates the DNS resolution process to redirect users to malicious websites. By altering DNS records, attackers can trick users into visiting fraudulent sites that may steal data or distribute malware.
How DNS Spoofing Works
DNS spoofing involves tampering with the DNS resolution process. Here’s a simplified overview:
- An attacker compromises a DNS server or intercepts a DNS request.
- They inject false DNS records, mapping a legitimate domain to a malicious IP address.
- When a user attempts to visit the legitimate site, they are redirected to the attacker's site.
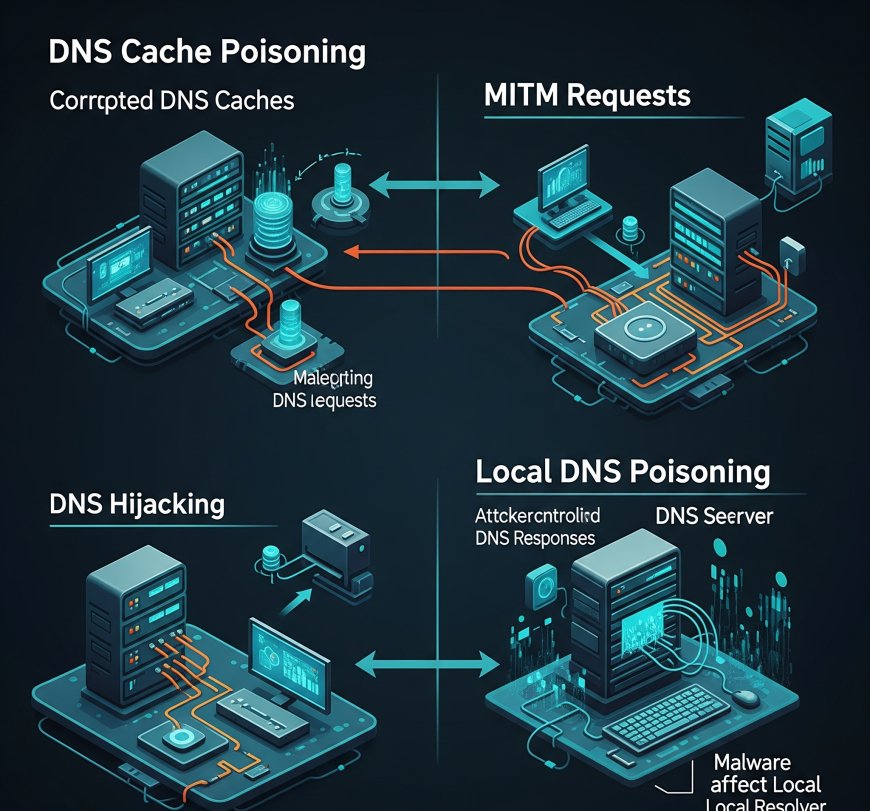
Types of DNS Spoofing Attacks
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| DNS Cache Poisoning | Corrupts the cache of a DNS resolver with false information. |
| Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) | Intercepts DNS requests and responses to provide malicious IP addresses. |
| DNS Hijacking | Takes control of a DNS server to redirect traffic to malicious sites. |
| Local DNS Poisoning | Targets a user’s local DNS settings, often via malware. |
Impact of DNS Spoofing
DNS spoofing can have severe consequences, including:
- Data Theft: Users may unknowingly provide sensitive information to fake websites.
- Malware Distribution: Redirected sites can infect devices with malware.
- Financial Loss: Stolen credentials can lead to unauthorized transactions.
- Reputation Damage: Businesses targeted by spoofing may lose customer trust.
Prevention Measures
Protecting against DNS spoofing requires proactive steps. Here are some effective measures:
| Measure | Description |
|---|---|
| Use DNSSEC | Domain Name System Security Extensions (DNSSEC) validates DNS responses to ensure authenticity. |
| Secure DNS Servers | Regularly update and patch DNS servers to prevent vulnerabilities. |
| Use Trusted DNS Providers | Opt for reputable DNS providers like Cloudflare or Google Public DNS. |
| Enable HTTPS | HTTPS websites can help detect spoofed sites through certificate mismatches. |
| Educate Users | Train users to recognize phishing attempts and verify website authenticity. |
Real-World Examples
DNS spoofing has been used in several high-profile attacks:
- 2019 MyEtherWallet Attack: Attackers redirected users to a phishing site, stealing cryptocurrency worth thousands of dollars.
- 2018 Banco de Chile Attack: DNS spoofing facilitated a $10 million heist by redirecting bank traffic to malicious servers.
Conclusion
DNS spoofing is a serious cybersecurity threat that can compromise personal and organizational data. By understanding how it works, recognizing its impact, and implementing preventive measures like DNSSEC and secure DNS providers, you can significantly reduce your risk. Stay vigilant, educate yourself and others, and adopt robust security practices to navigate the internet safely.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is DNS spoofing?
DNS spoofing is a cyberattack where an attacker alters DNS records to redirect users to fake or malicious websites without their knowledge.
How does DNS spoofing differ from phishing?
DNS spoofing manipulates the DNS system to mislead users, while phishing typically involves tricking users into clicking fake links or giving up sensitive information through emails or messages.
Can DNS spoofing be detected?
Yes, with the help of advanced security tools, anomaly detection systems, and DNSSEC validation, DNS spoofing can often be identified.
Who is at risk of DNS spoofing?
Any internet user, especially those on unsecured networks like public Wi-Fi, is at risk of DNS spoofing attacks.
What is DNSSEC?
DNSSEC (Domain Name System Security Extensions) is a protocol that adds a layer of authentication to DNS responses to prevent spoofing and tampering.
Can VPNs prevent DNS spoofing?
VPNs encrypt your internet traffic and can help prevent DNS spoofing by forcing DNS requests through secure tunnels, especially when using trusted DNS servers.
How can I tell if a website is spoofed?
Check for HTTPS, look for certificate warnings, and verify the domain name carefully. Spoofed sites often have small typos or missing security indicators.
What is cache poisoning?
Cache poisoning is a technique used in DNS spoofing where attackers inject false information into a DNS cache, causing users to be redirected to malicious sites.
Can antivirus software prevent DNS spoofing?
Antivirus software may detect and block malicious websites or DNS-related malware, but it cannot always prevent DNS spoofing on its own.
What should I do if I suspect DNS spoofing?
Disconnect from the network, flush your DNS cache, switch to a trusted DNS provider (like Google or Cloudflare), and run a malware scan.
Is DNS spoofing illegal?
Yes, DNS spoofing is a form of cybercrime and is illegal in most countries under laws related to computer misuse and unauthorized access.
Can DNS spoofing affect mobile devices?
Yes, mobile devices can also be targeted through rogue Wi-Fi networks, malicious apps, or modified DNS settings.
How common is DNS spoofing?
While not as common as phishing, DNS spoofing is still a prevalent threat, especially in targeted attacks and unsecured networks.
Can I use public Wi-Fi safely to avoid DNS spoofing?
To reduce risk, avoid logging into sensitive accounts over public Wi-Fi, use a VPN, and prefer secure HTTPS connections.
What tools do attackers use for DNS spoofing?
Attackers may use tools like Ettercap, DNSChef, or custom scripts to carry out DNS spoofing and cache poisoning attacks.
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0















